Explodable 3D Dog Skull for Veterinary Education
3D models of a Sheep and Goat Skull and Inner ear
3D models of Miocene vertebrates from Tavers
3D GM dataset of bird skeletal variation
Skeletal embryonic development in the catshark
Bony connexions of the petrosal bone of extant hippos
bony labyrinth (11) , inner ear (10) , Eocene (8) , South America (8) , Paleobiogeography (7) , skull (7) , phylogeny (6)
Lionel Hautier (23) , Maëva Judith Orliac (21) , Laurent Marivaux (16) , Rodolphe Tabuce (14) , Bastien Mennecart (13) , Pierre-Olivier Antoine (12) , Renaud Lebrun (11)
MorphoMuseuM Volume 04, issue 01
<< prev. article next article >>
|
3D dataset3D models related to the publication: Evolutionary Adaptation to Aquatic Lifestyle in Extinct Sloths Can Lead to Systemic Alteration of Bone Structure.Eli Amson
Published online: 09/05/2018 |
|
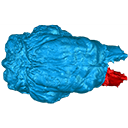
M3#337Brain endocast Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.337 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Choloepus didactylus MNHN-ZM-MO-1996-594 View specimen
|
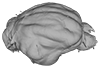
M3#338Brain endocast Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.338 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Thalassocnus natans MNHN-F-SAS-734 View specimen

|
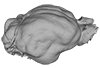
M3#339Brain endocast Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.339 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Thalassocnus littoralis MNHN-F-SAS-1610 View specimen
|
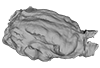
M3#340Brain endocast Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.340 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Thalassocnus littoralis MNHN-F-SAS-1615 View specimen

|
M3#341Brain endocast Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.341 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Thalassocnus carolomartini SMNK-3814 View specimen

|
M3#342Brain endocast lacking right olfactory bulb Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.342 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Amson, E., Billet, G., de Muizon, C., under review. Evolutionary Adaptation to Aquatic Lifestyle in Extinct Sloths Can Lead to Systemic Alteration of Bone Structure. Proceedings of the Royal Society B. doi:10.1098/rspb.2018.0270
Cignoni P., Callieri M., Corsini M., Dellepiane M., Ganovelli F., Ranzuglia G., 2008. MeshLab: an Open-Source Mesh Processing Tool. In Eurographics Italian Chapter Conference (eds V Scarano, R De Chiara, U Erra), The Eurographics Association. doi:10.2312/LocalChapterEvents/ItalChap/ItalianChapConf2008/129-136